Injuries to the brain are some of the most severe injuries to happen to a person after a terrible accident including car, truck, motorcycle, and work accidents and can lead to lifelong injuries or even a risk of death.
The Brain Injury Attorneys at Miller Weisbrod represent clients nationwide who have suffered severe brain injuries due to the negligence of others. From serious car accidents to workplace accidents, we put our experience and resources to work to achieve maximum compensation on behalf of our clients.
The consequences from a brain injury are unpredictable, and can change everything about us in a matter of seconds. The brain is made up of many parts, each with a specific and important function.
It controls our ability to balance, walk, talk, and eat. Our brain coordinates and regulates our breathing, blood circulation, and heart rate. It is responsible for our ability to speak, to process and remember information, make decisions, and feel emotions. Every brain is unique, ever-changing, and extremely sensitive to its environment.
BRAIN FUNCTIONS
The brain is a complex organ that controls thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body. Together, the brain and spinal cord that extends from it make up the central nervous system, or CNS.
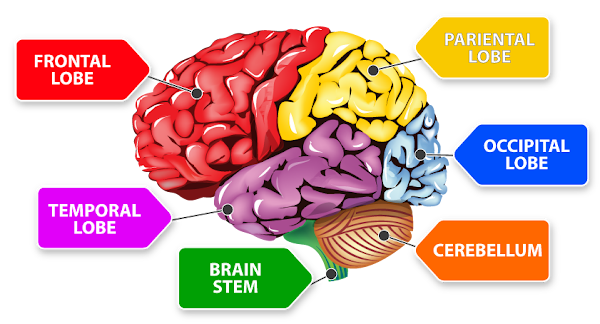
Injuries to these sections (or lobes) can have different effects based upon what part of functions they control.
Lobe Functions
FRONTAL LOBE
An injury to the frontal lobes may affect an individual’s ability to control emotions, impulses, and behavior or may cause difficulty recalling events or speaking.
- Attention
- Concentration
- Self-Monitoring
- Organization
- Expressive Language (Speaking)
- Motor Planning & Initiation
- Awareness of Abilities
- Awareness of Limitations
- Personality
- Mental Flexibility
- Inhibition of Behavior
- Emotions
- Problem Solving
- Planning
- Judgment
TEMPORAL LOBE
An injury to the temporal lobes may lead individuals to demonstrate difficulty with communication or memory.
- Memory
- Understanding Language (Receptive Language)
- Sequencing
- Hearing
- Organization
PARIETAL LOBE
Individuals who have injured their parietal lobes may have trouble with their five primary senses.
- Sense of Touch
- Spatial Perception (Depth Perception)
- Identification of Sizes, Shapes, Colors
- Visual Perception
OCCIPITAL LOBE
An injury to one’s occipital lobes may lead to trouble seeing or perceiving the size and shape of objects.
- Vision
CEREBELLUM
The brain stem controls the body’s involuntary functions that are essential for survival, such as breathing and heart rate.
- Breathing
- Arousal
- Consciousness
- Heart Rate
- Sleep & Wake Cycles
BRAIN INJURY TYPES
Brain injuries may be classified as traumatic or non-traumatic to describe the cause of the injury. They may also be classified as mild, moderate, or severe to indicate the initial severity of the injury. Other terms, such as diffuse or penetrating, may be used to describe the type injury.
As experienced Personal Injury Attorneys, Miller Weisbrod understands the devastating, and often life-long impact traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) can have on individuals and their families. We take a proactive approach to ensure our clients' immediate and future needs are covered by any verdict or settlement.
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is defined as an alteration in brain function, or other evidence of brain pathology, caused by an external force. Traumatic impact injuries can be defined as closed (or non-penetrating) or open (penetrating).
Often referred to as an acquired brain injury, a non-traumatic brain injury causes damage to the brain by internal factors, such as a lack of oxygen, exposure to toxins, pressure from a tumor, etc. Read on for an overview of some of the common causes of brain injury.
BRAIN INJURY CAUSES
| Traumatic Causes | Traumatic Causes |
|---|---|
| Falls | Stroke (Hemorrhage, Blood Clot) |
| Assaults | Infectious Disease |
| Motor Vehicle Accidents | Meningitis |
| Sports/Recreation Injuries | Encephalitis |
| Abusive Head Trauma (Shaken Baby Syndrome) | Seizure |
| Gunshot Wounds | Electric Shock |
| Workplace Injuries | Tumors |
| Child Abuse | Metabolic Disorders |
| Domestic Violence | Neurotoxic Poisoning (Carbon Monoxide, Lead Exposure) |
| Military Actions (Blast Injury) | Lack of Oxygen (Drowning, Choking) |
| Hypoxic/Anoxic Injury – including during birth | |
| Drug Overdose |
BRAIN INJURY SYMPTOMS
Signs of brain trauma can vary. One may experience physical symptoms or functional and emotional changes if a traumatic or non-traumatic brain injury has occurred.
After an impact or injury to the head, an individual can experience a variety of symptoms.
Common symptoms of a brain injury include:
- Loss of consciousness, or altered consciousness (“state of confusion”)
- Dilated eyes (the black center of the eye is large and does not get smaller in light) or unequal size of pupils
- Vision changes (blurred vision or seeing double, not able to tolerate bright light, loss of eye movement, blindness)
- Dizziness
- Balance problems
- Vomiting
- Lethargy
- Headache
- Confusion
- Weakness
- Poor coordination
- Rnging in the ears (tinnitus) or changes in ability to hear
- Difficulty with thinking skills (difficulty “thinking straight”, memory problems, poor judgment, poor attention span, a slowed thought processing speed)
- Inappropriate emotional responses (irritability, easily frustrated, inappropriate crying or laughing)
- Difficulty speaking (slurred speech, difficulty swallowing)
- Spinal fluid (thin, clear liquid) coming out of the ears or nose
- Respiratory failure (difficulty breathing)
- Coma (not alert and unable to respond to others) or semi-comatose state
- Paralysis or difficulty moving body parts
- Slow pulse
- Slow breathing rate, with an increase in blood pressure
- Body numbness or tingling
- Loss of bowel control or bladder control
*If you are experiencing any of these signs of brain trauma, contact your doctor immediately.
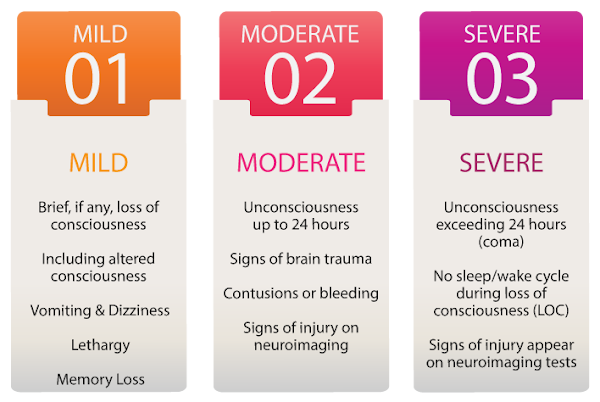
BRAIN INJURY SEVERITY
The severity of damage to the brain after an injury is the primary factor in predicting the injury’s impact on the individual. Brain injury is typically categorized as mild, moderate, or severe.
A severe brain injury may cause the individual to experience an unconscious state, where one appears to be in a deep sleep and cannot be aroused or respond purposefully. Assessments will typically reveal that the individual has no sleep and wake cycles. This loss of consciousness (LOC) is referred to as a coma. Depending on varying factors and the severity of injury, the individual may remain in a coma, emerge from a coma, or experience an increased level of consciousness.
People can, however, experience different states of consciousness after brain injury. Understanding these disorders of consciousness can be important when discussing treatment and possible rehabilitation options.
Vegetative State
An individual is unaware, but begins to have sleep and wake cycles; normal digestion, breathing, and heart rates; and may open his or her eyes. The individual may occasionally respond to stimuli.
Persistent Vegetative State
Doctors consider a person to be in a persistent vegetative state one year after traumatic brain injury or three to six months after a hypoxic or anoxic brain injury.
Minimally Conscious State
An individual shows slight but definite self-awareness or awareness of their environment.
They may inconsistently speak short phrases or words, respond to simple commands, may make “yes or no” gestures or verbalizations (sometimes incorrectly), follow people with their eyes, grasp or hold objects, and show appropriate emotional responses, such as smiling or crying.
One person may only demonstrate a few of these behaviors, while others exhibit all of them. A minimally responsive state may be a transition level to a higher level of consciousness. An individual is considered out of a minimally conscious state if he or she can communicate consistently (at least “yes” and “no”) or can use common objects, such as a glass or brush.
Locked-in Syndrome
An individual can only move his or her eyes, not any other part of their body, and is conscious and able to think.
Diagnosing brain injury and determining injury severity are two different things. In cases where the injury is more severe, it is usually clear from the individual’s symptoms that some type of brain injury has occurred. In situations where the brain injury is mild or moderate, further assessment is often needed to diagnose the brain injury.
CONTACT MILLER WEISBROD
If you or a loved one has suffered a brain injury after any type of accident, do not hesitate to contact the experienced Dallas injury attorneys at Miller Weisbrod, Attorneys At Law.
Our injury attorneys have the proven record, experience, and resources to help you achieve the compensation you deserve. Contact our offices in Dallas, today at (214) 987-0005 for your initial free consultation. You may also complete the form on this page to contact our support team.